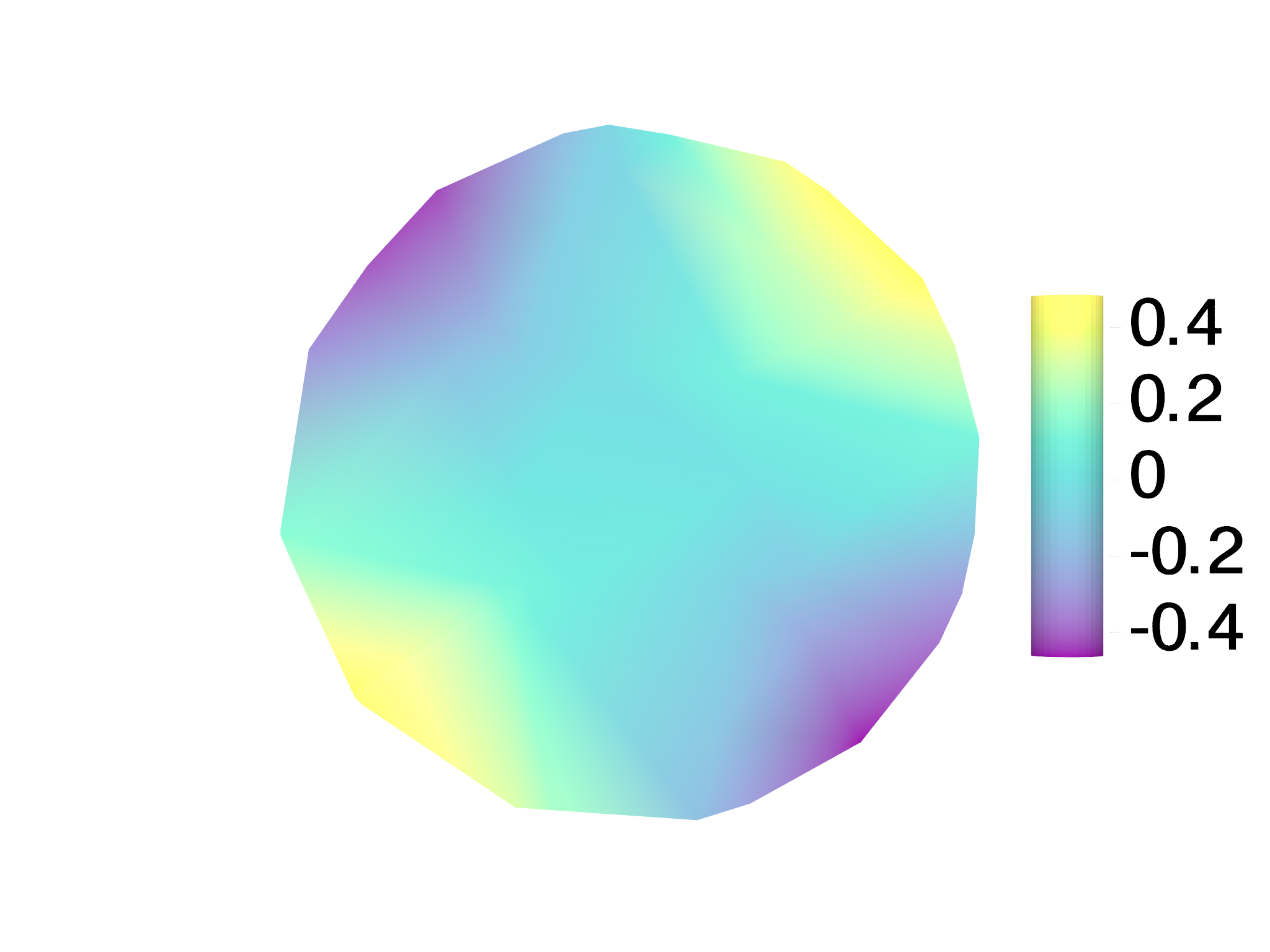Slicing meshes
The meshslice module is designed to help visualize a "slice" through
the mesh and associated Fields, which is often useful when working with
three or higher dimensional meshes. To illustrate its use, we'll reuse
the spherical mesh created with MeshGen in the Meshgen Section above (see Fig.
5.3).
Ensure that the mesh has grade 2 elements present with addgrade if
necessary. We'll also create a simple scalar field:
var u = Field(m, fn (x,y,z) x*y)
To take a slice, first create a MeshSlicer object with the mesh we want to slice:
var ms=MeshSlicer(m)
Then call the slice method, which requires us to specify a slicing
plane. Planes are defined by a point \((x,y,z)\) and a normal vector
\((n_{x},n_{y},n_{z})\), which are passed as arguments:
var slc=ms.slice([0,0,0],[0,0,1]) // position, normal
After taking a slice, we can then slice any number of Field objects as well:
var uslc=ms.slicefield(u)
A single MeshSlicer can take any number of slices from the same Mesh;
slicefield always uses the most recent slice taken. Results from the
example are shown in Fig. 5.12. As can be seen, the results of slicing a
Mesh typically produce meshes that are quire irregular, with narrow
triangles and unequally sized elements. Hence, these meshes are intended
mostly for visualization purposes rather than use in calculations.