Catenoid
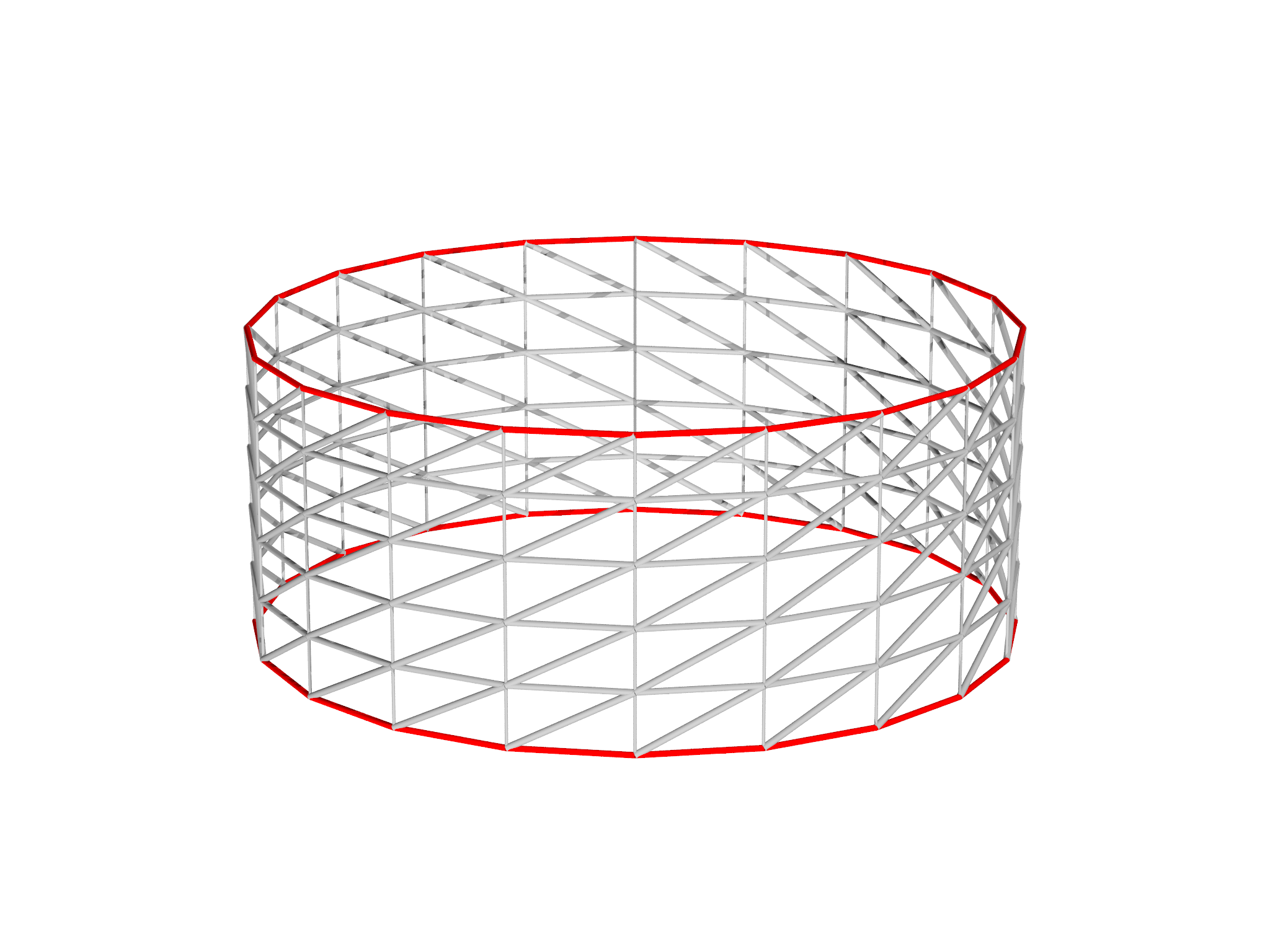
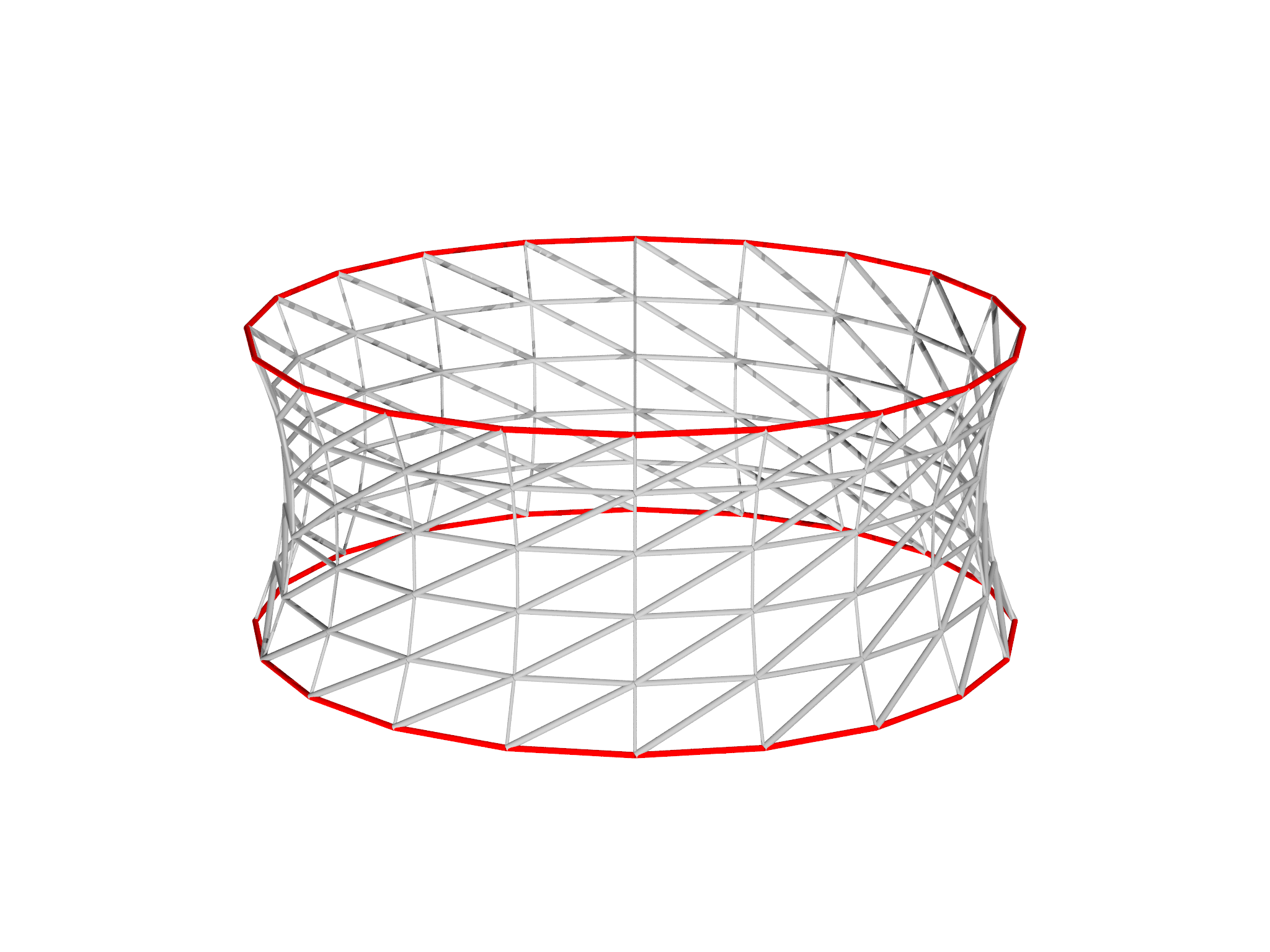
A soap film held between two parallel concentric circular rings adopts the shape of a minimal surface called a catenoid. This is a relatively simple optimization problem, and hence is a good example for beginners to morpho.
The initial mesh is created using AreaMesh in the meshtools module:
var r = 1.0 // radius
var ratio = 0.4 // Separation to diameter ratio
var L = 2*r*ratio // Separation
// Generate a tube / cylindrical mesh
var mesh = AreaMesh(fn (u, v) [r*cos(u), v, r*sin(u)],
-Pi...Pi:Pi/10,
-L/2..L/2:L/5,
closed=[true,false] )
mesh.addgrade(1)
The boundary of the mesh must be fixed in place. We can do this by creating a Selection, and visualizing it as shown in Fig. 7.1, left panel:
// Select the boundary
var bnd = Selection(mesh, boundary=true)
var g = plotselection(mesh, bnd, grade=1)
The optimization problem simply requires us to specify the area as the quantity to minimize:
// Define the optimizataion problem
var problem = OptimizationProblem(mesh)
// Add the area energy using the built-in Area functional
var area = Area()
problem.addenergy(area)
We then create a ShapeOptimizer to perform the optimization,
var opt = ShapeOptimizer(problem, mesh)
fix the boundary elements using the selection object we created,
opt.fix(bnd)
and perform the optimization. Conjugate gradient works well for this problem and converges in a few iterations. The final optimized shape is shown in Fig. 7.1, right panel.
opt.conjugategradient(1000)